The traditional electronic-ballot-to-blockchian voting method is vulnerable to undetectable and large-scale hacks and would require a whole new election if the electronic ballots or blockchain were hacked because no paper ballots would exist for a hand-count or otherwise.
-
PaperBallotchain Whitepaper
A Verifiable & Transparent Voting System
PaperBallotchain is a paper-first ballot custody and verification system that strengthens election integrity through transparent, auditable chain-of-custody controls without replacing existing voting processes.
PaperBallotchain is not a cryptocurrency or internet-based voting platform—PaperBallotchain is a paper-first chain-of-custody and verification framework designed to strengthen existing election laws and procedures.
You don’t need to understand blockchain technology to trust PaperBallotchain
because you can privately verify that your scanned paper ballot has
been added to the blockchain using your Paper Ballot ID#.
(Meanwhile, bad actors can’t verify which ballot you cast because
your Paper Ballot ID# could be any Paper Ballot ID# cast onto the
blockchain around the same time as yours from the same polling station.)
But if you're interested...
A blockchain is a specialized type of database—a cryptographically secure, transparent, immutable, tamper-evident, distributed, digital ledger.
Contents
What PaperBallotchain can solve for you
(Back to Contents)
Compare Voting Methods
(Back to Contents)
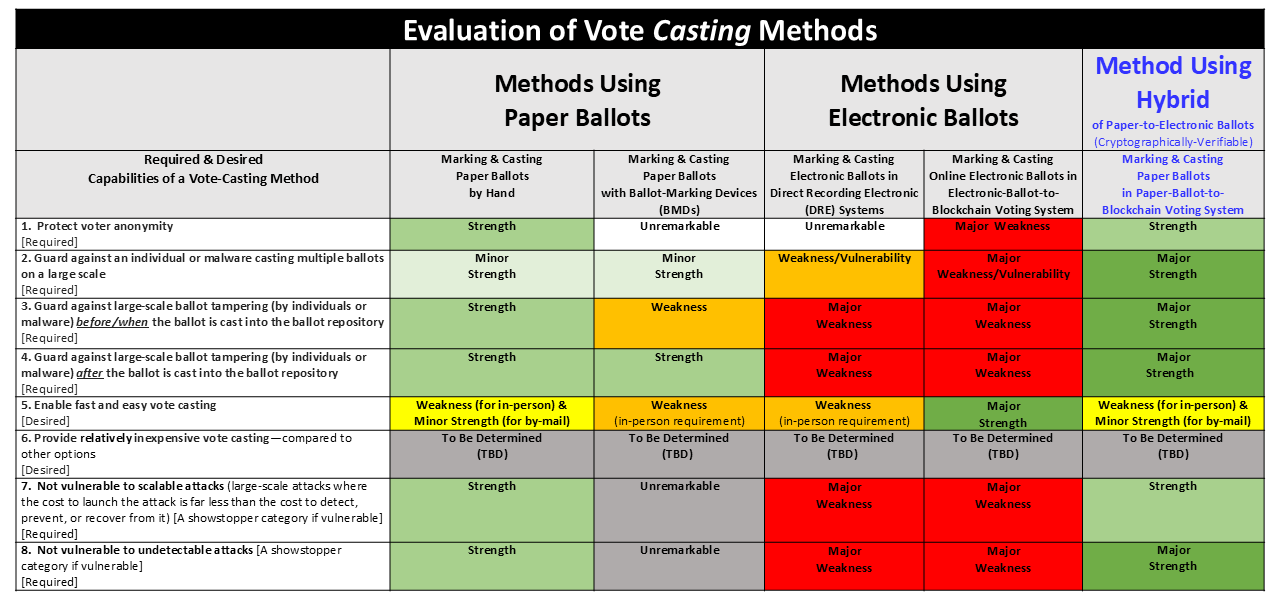
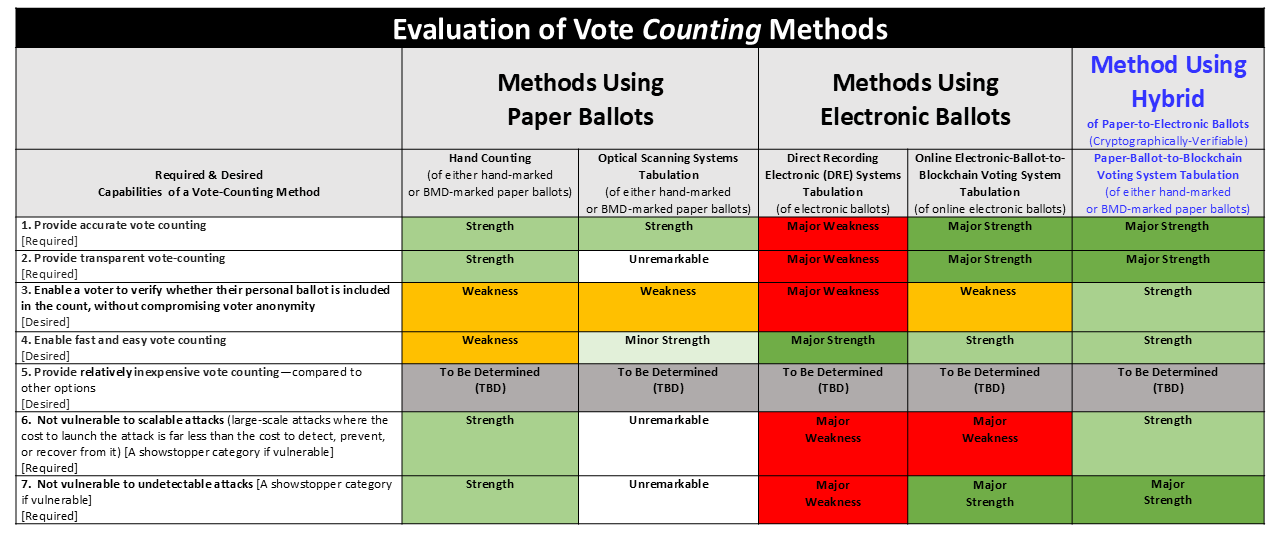
Summary
The Hybrid Paper-Ballot-to-Blockchain Voting method(the PaperBallotchain solution) has more strengths than the methods using only paper ballots or electronic ballots.
Solutions to problems in a system often come with tradeoffs.
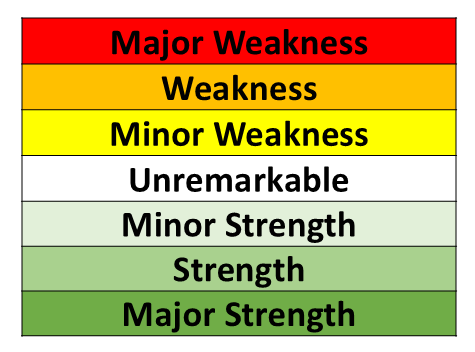
Rating Scale
Voters experience minimal change in paper-ballot-to-blockchain voting. Voters receive and cast paper ballots as they have done before. The main difference for voters is that they have the option to immediately look up their Ballot ID# on the live blockchain vote tallies report to confirm their ballot is included in the tallies—while giving voters plausible deniability about which Ballot ID# they cast because their Ballot ID# could be any Ballot ID# cast onto the blockchain around the same time as theirs from the same polling station, which would obfuscate bad actor efforts to verify which ballots were cast by which voters when seeking to buy or coerce votes. .
Compare Blockchain Voting Methods
(Back to Contents)
MIT and other Blockchain experts describe at least 14 key problems with electronic only blockchain voting. The first three problems (critical technical vulnerabilities) and PaperBallotchain’s solutions are described here. A description of the other 11 technical problems and PaperBallotchain’s solutions are available upon request.
Problems (Critical Technical Vulnerabilities)
in Traditional
Electronic-Ballot-to-Blockchain Voting
Solutions (Low-Tech & Non-Tech)
in New
Paper-Ballot-to-Blockchain Voting
Key Steps
in PaperBallotchain
(Back to Contents)
Security Layers that Ensure Voter Anonymity
Security Layers that Protect Ballot Integrity and Authenticity
Note: "Integrity" means the data has not been altered.
Note: "Authenticity" means the data can be verified as coming from an expected source
(in this case, verified cryptographically by 1) a Ballot Public Key that determines whether the ballot digital signature (created from the Ballot Private Key) is valid and 2) a Scanner Public Key that determines whether the scanner digital signature (created from the stakeholder Scanner Private Key) is valid).

